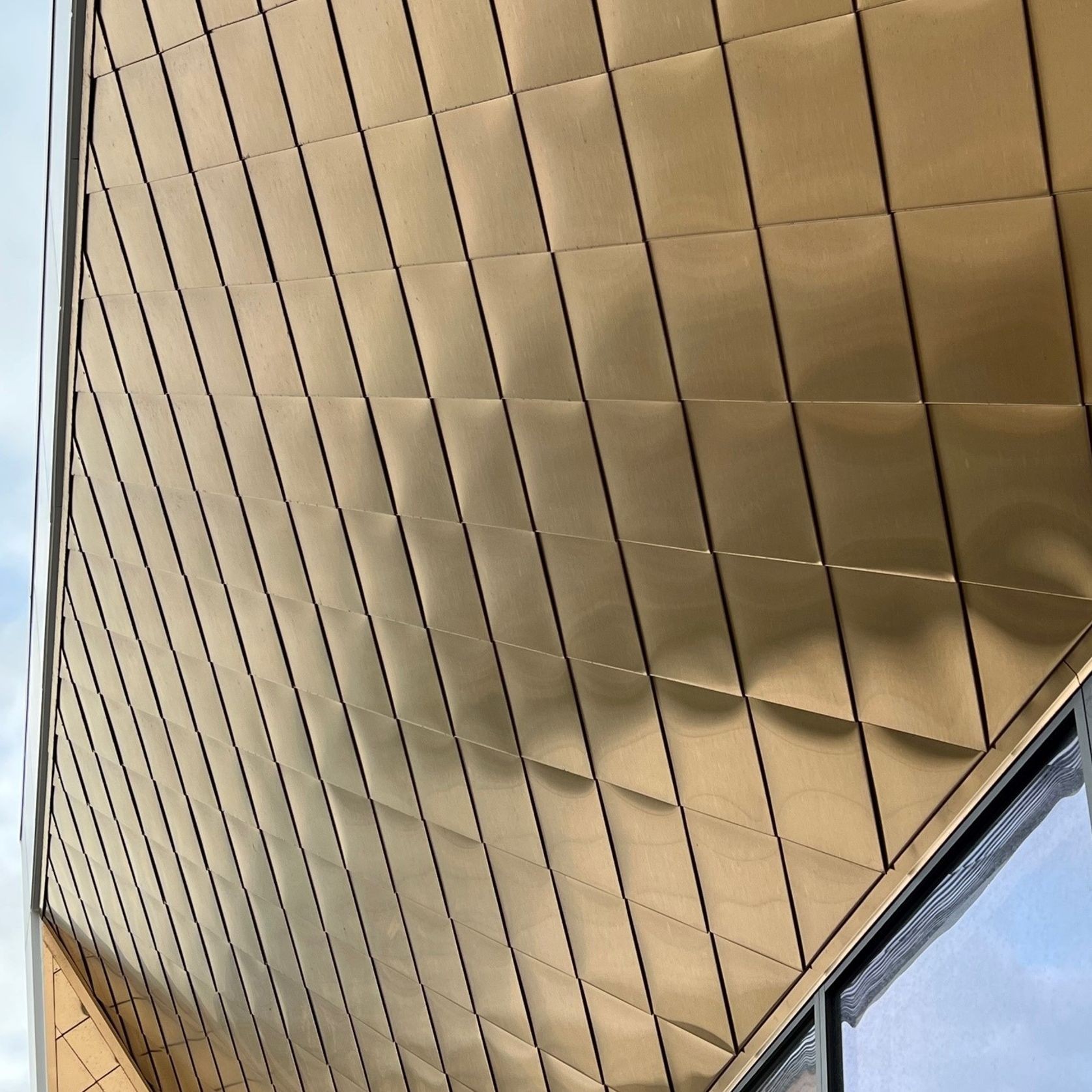
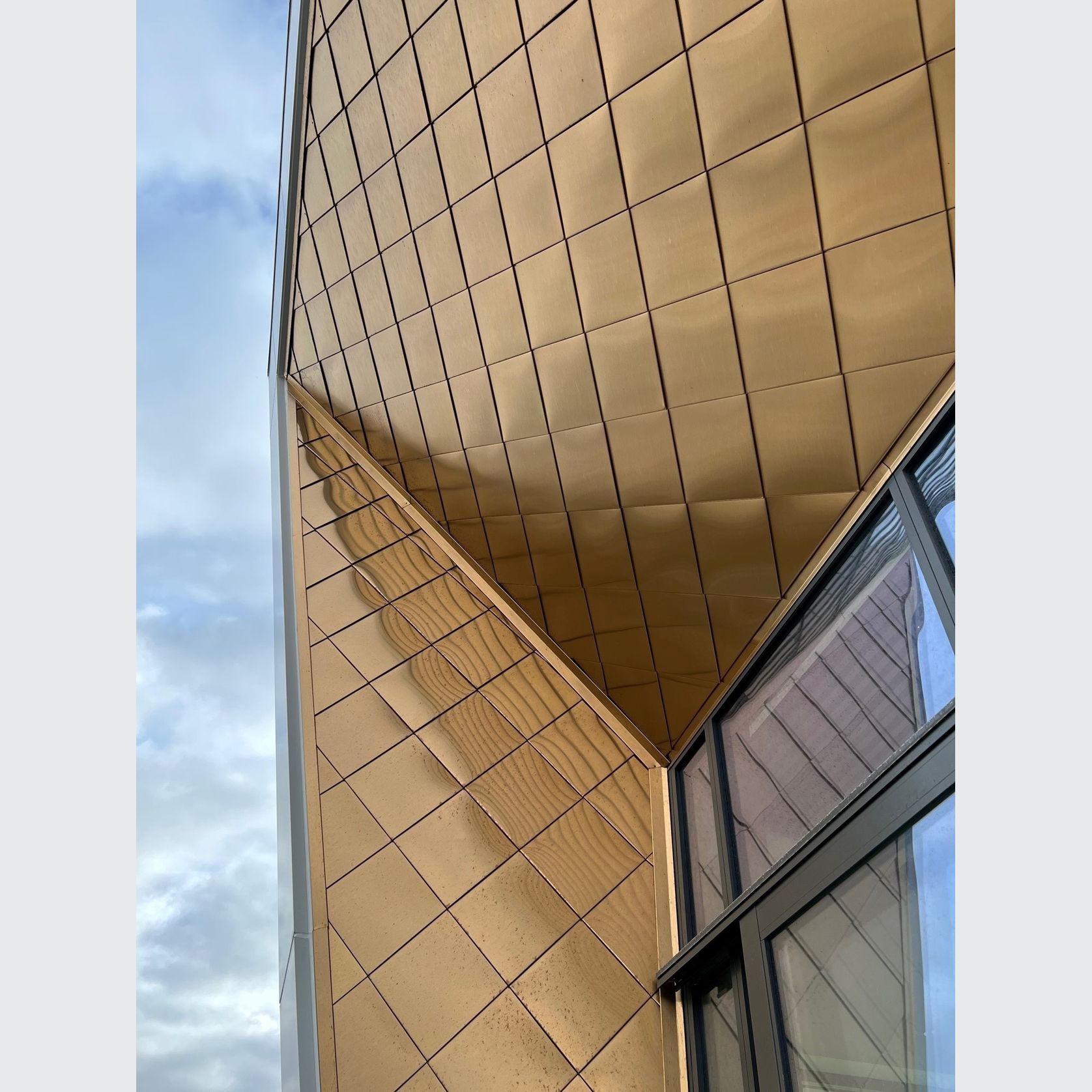
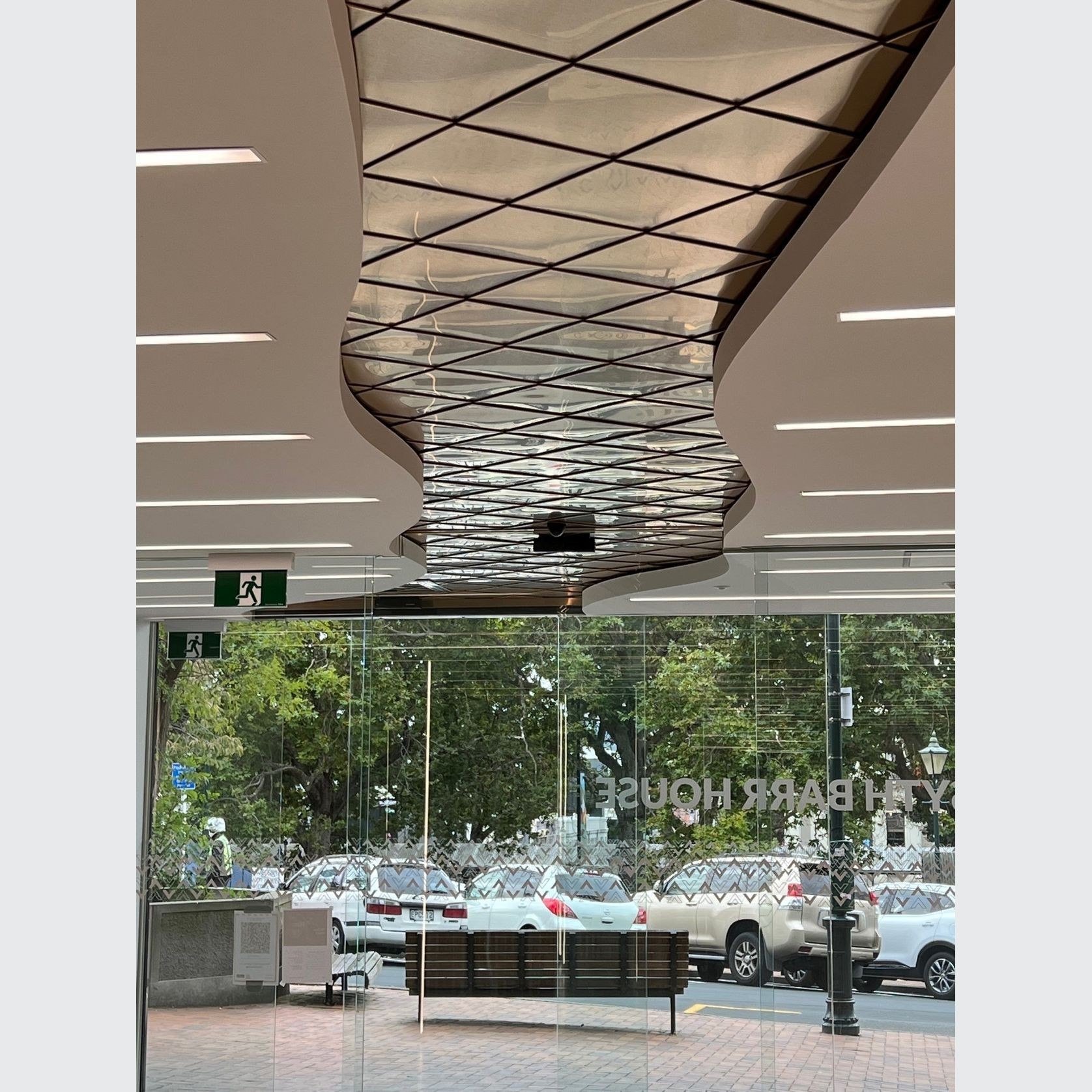
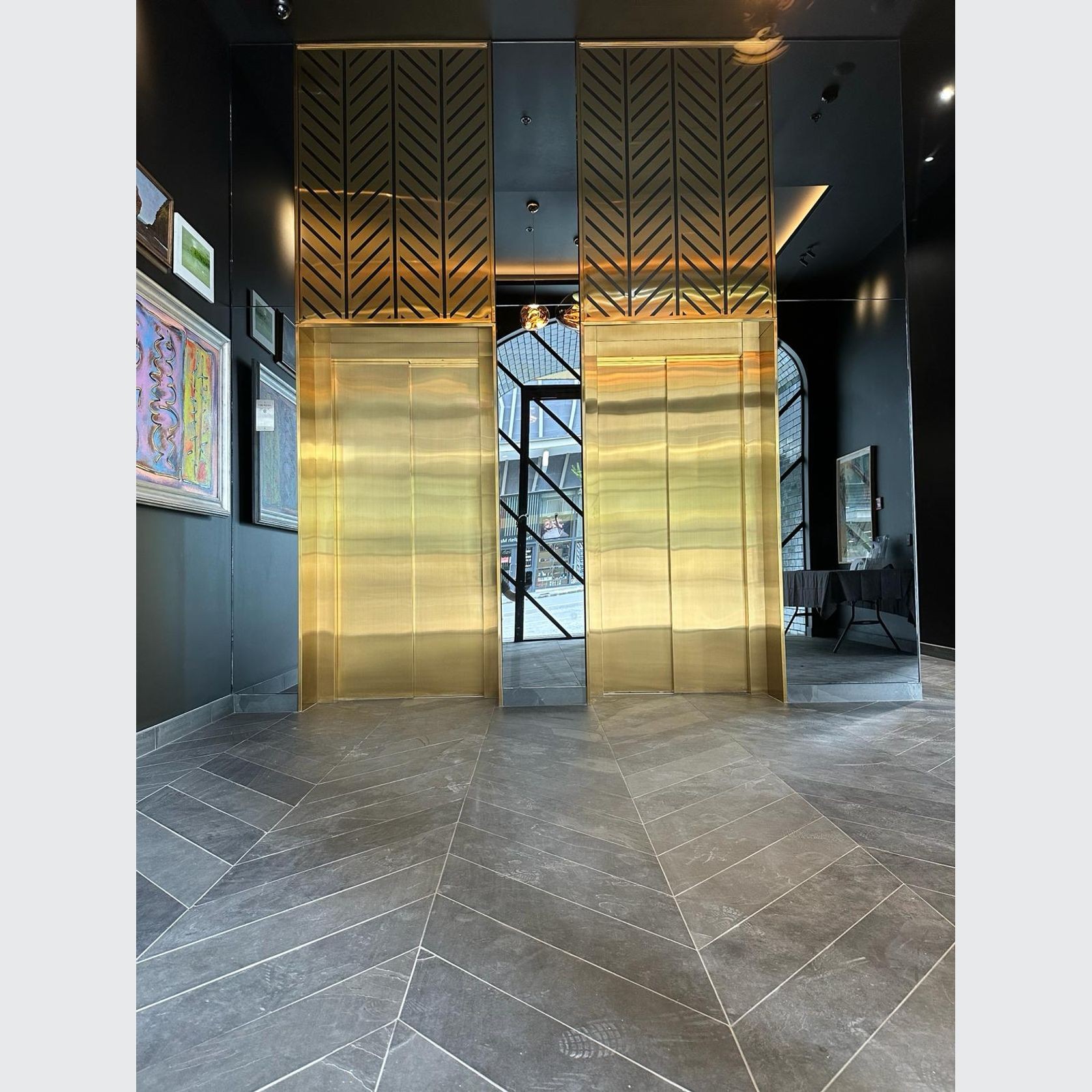
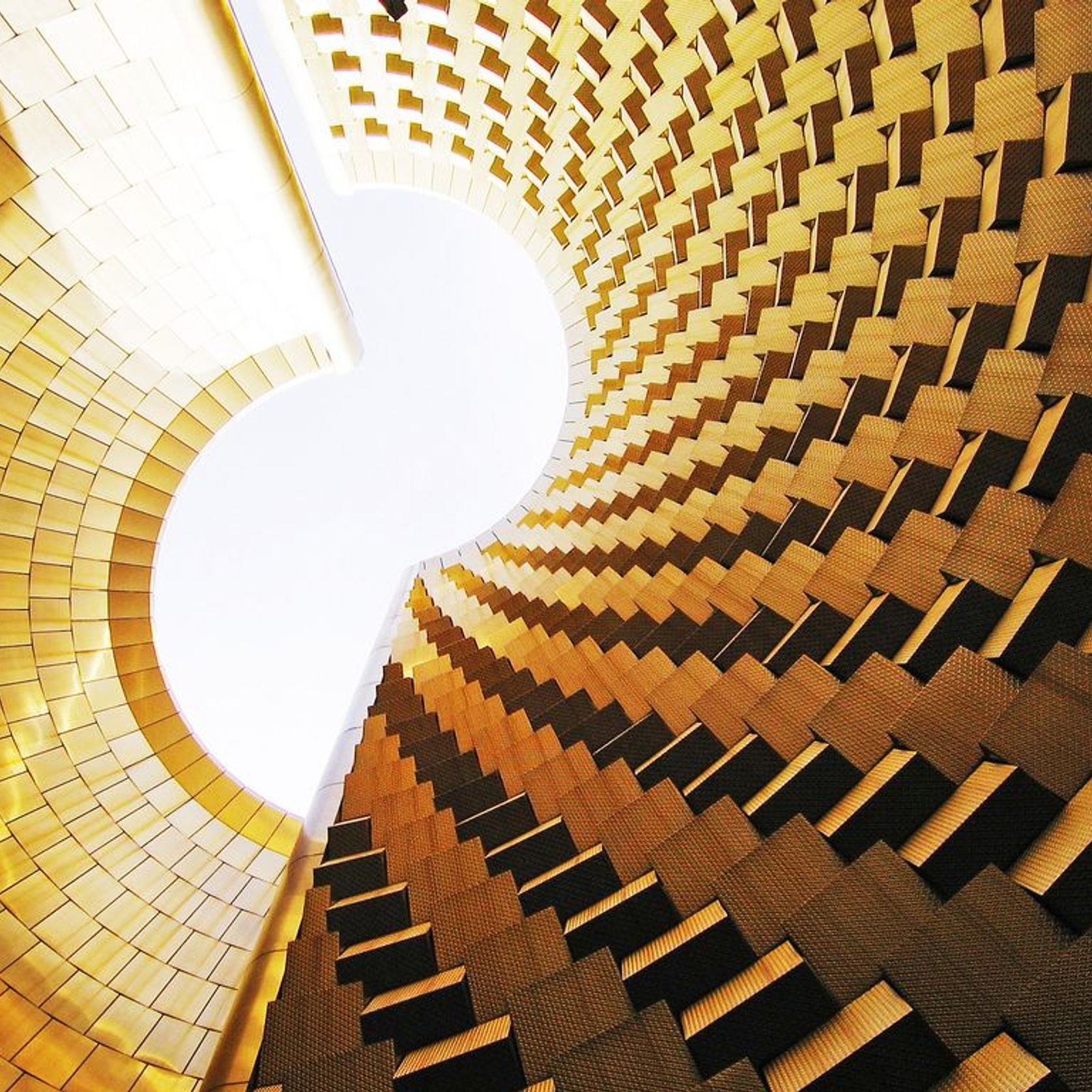
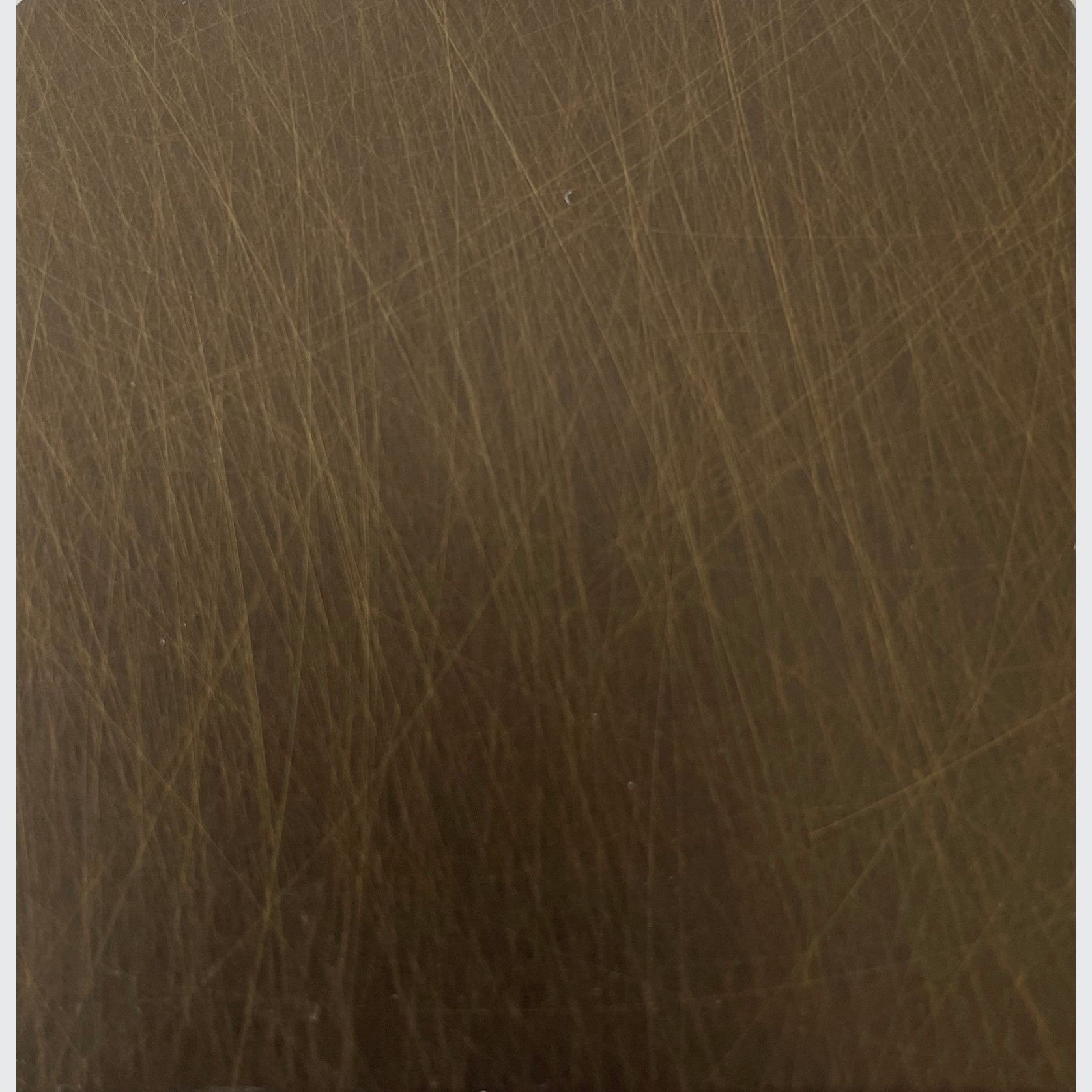
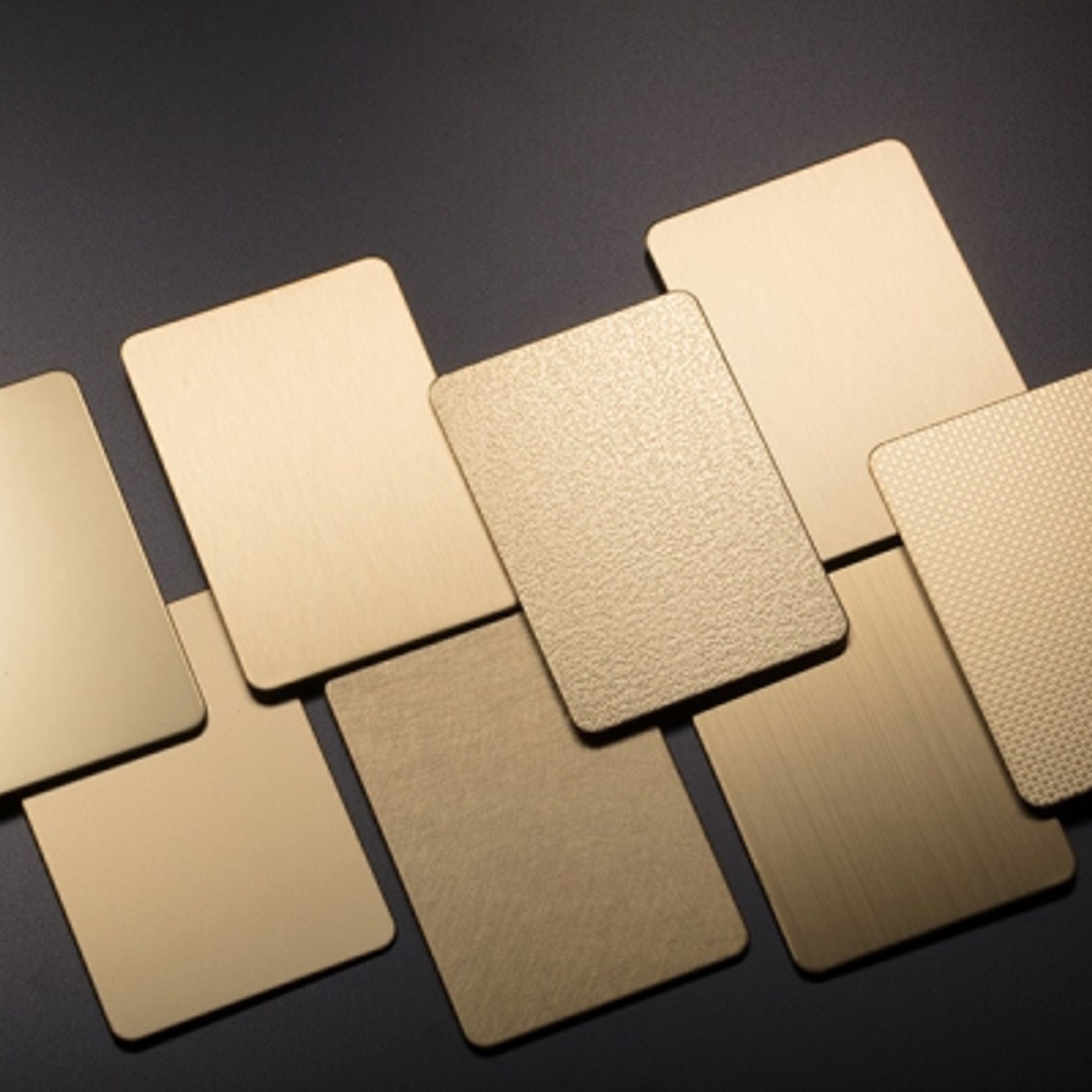
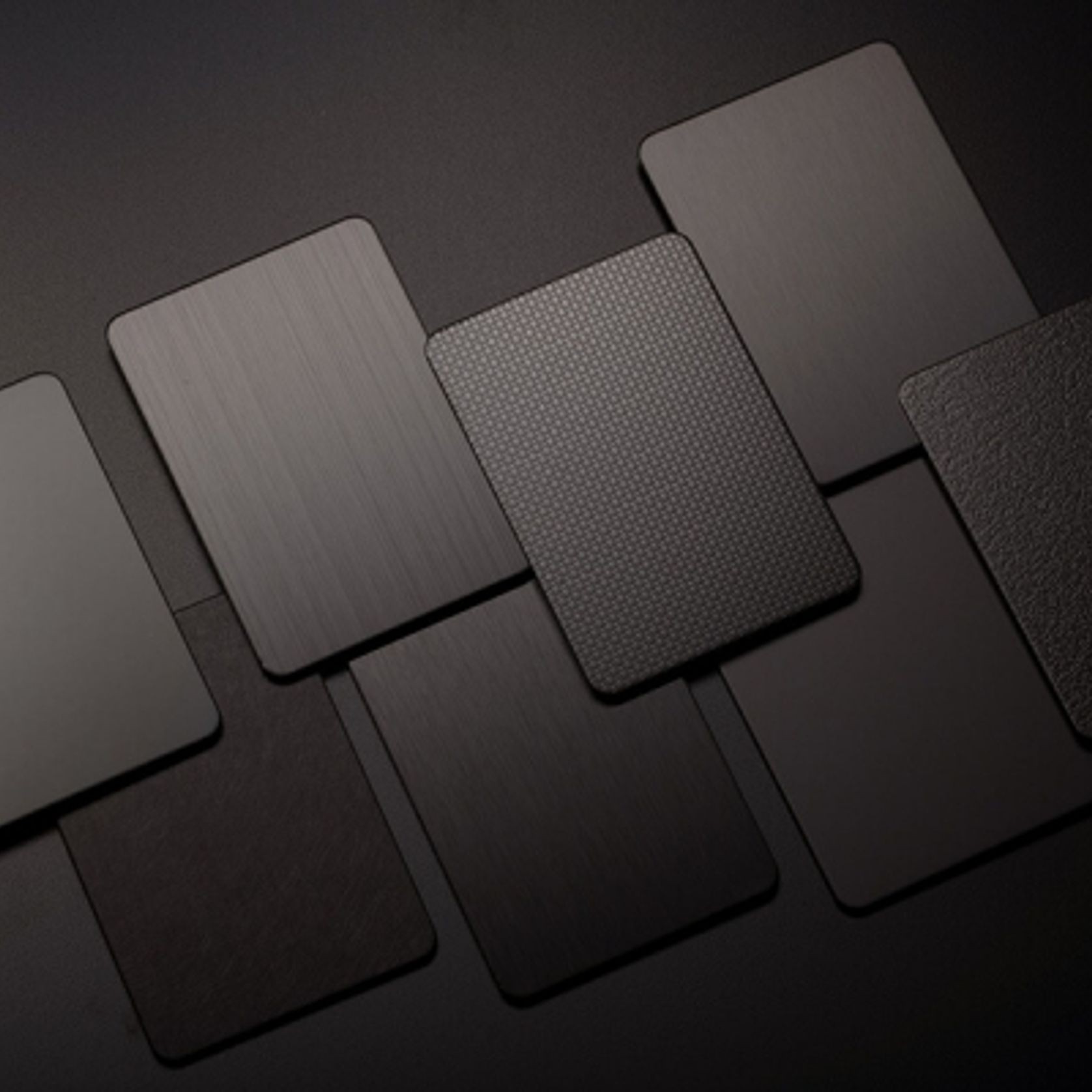
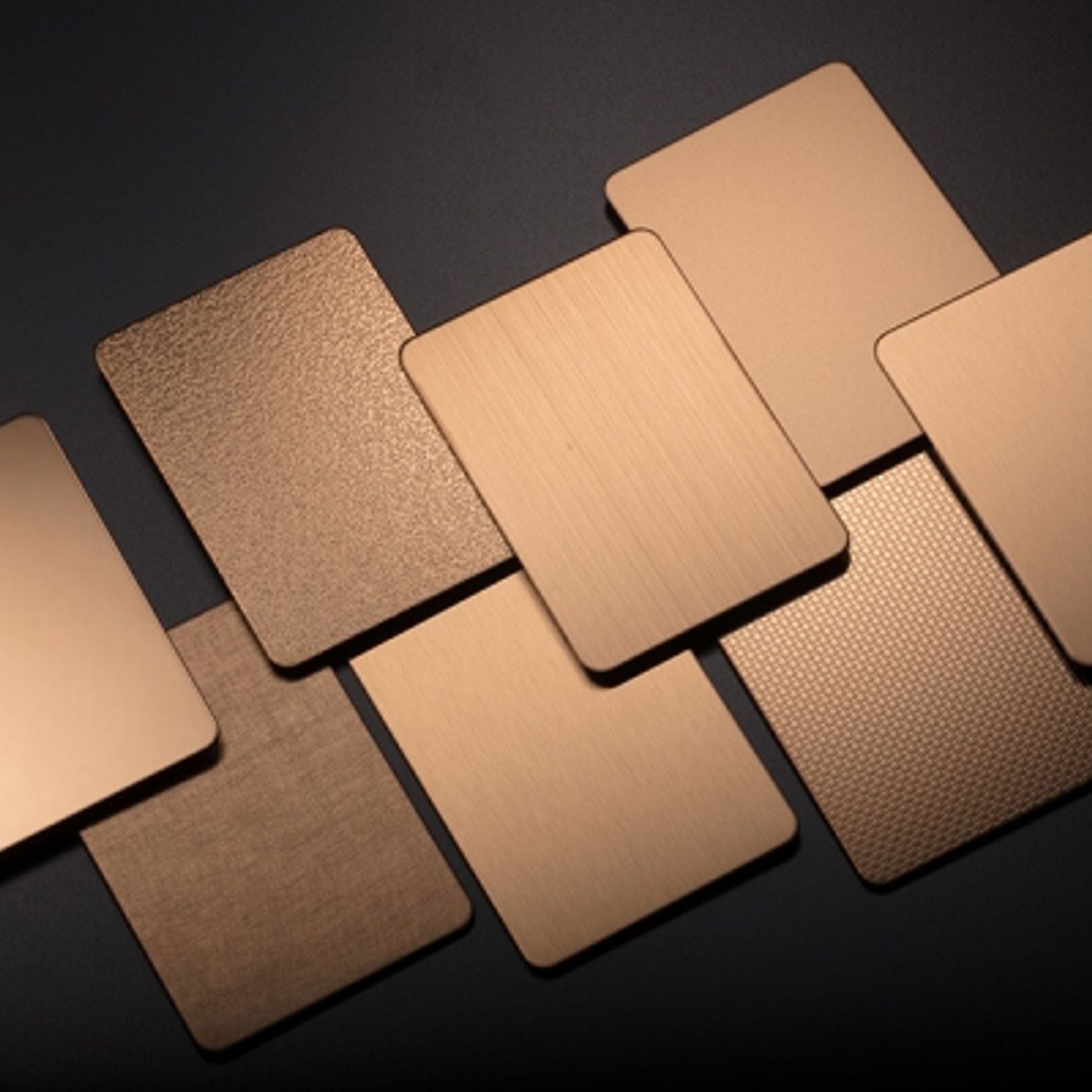
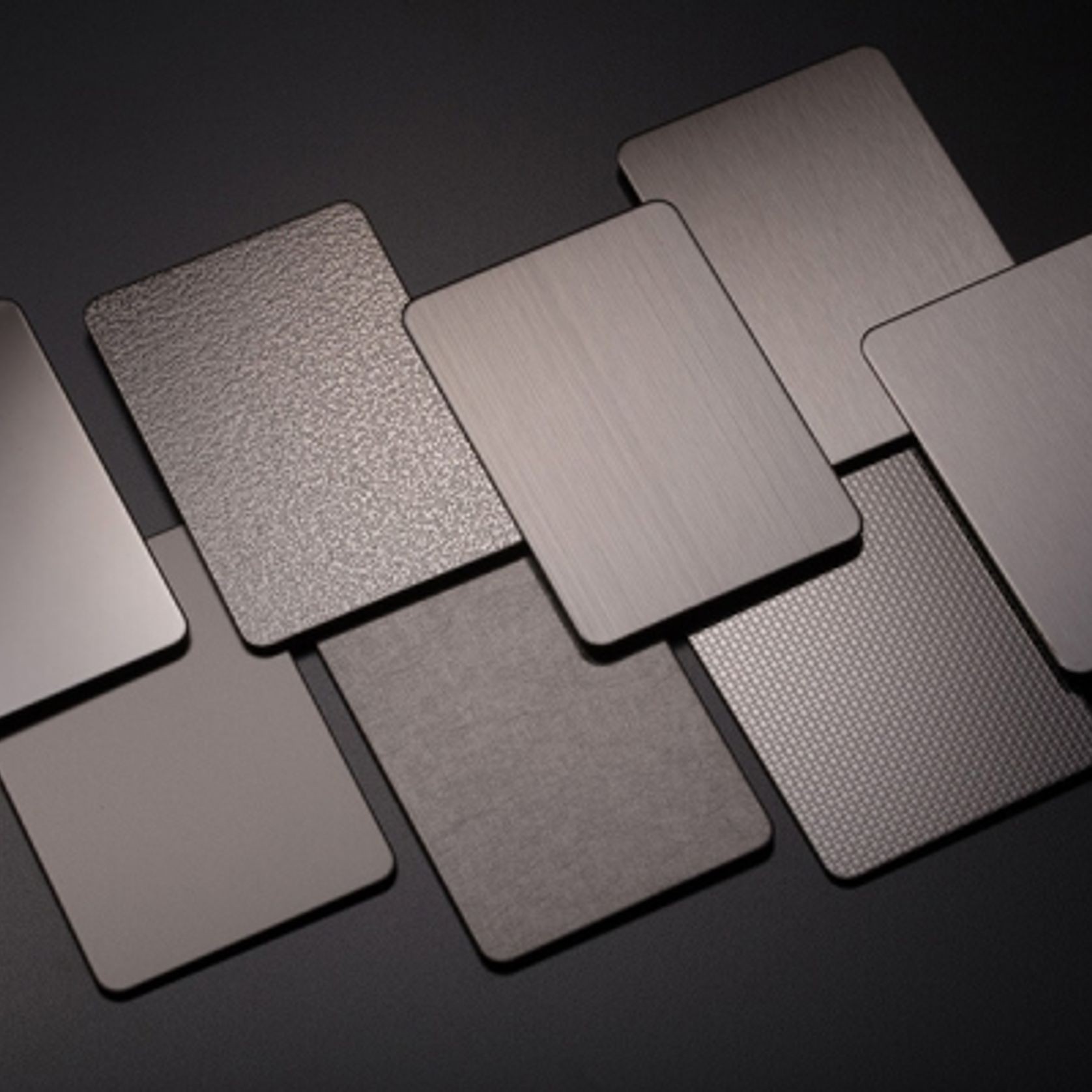
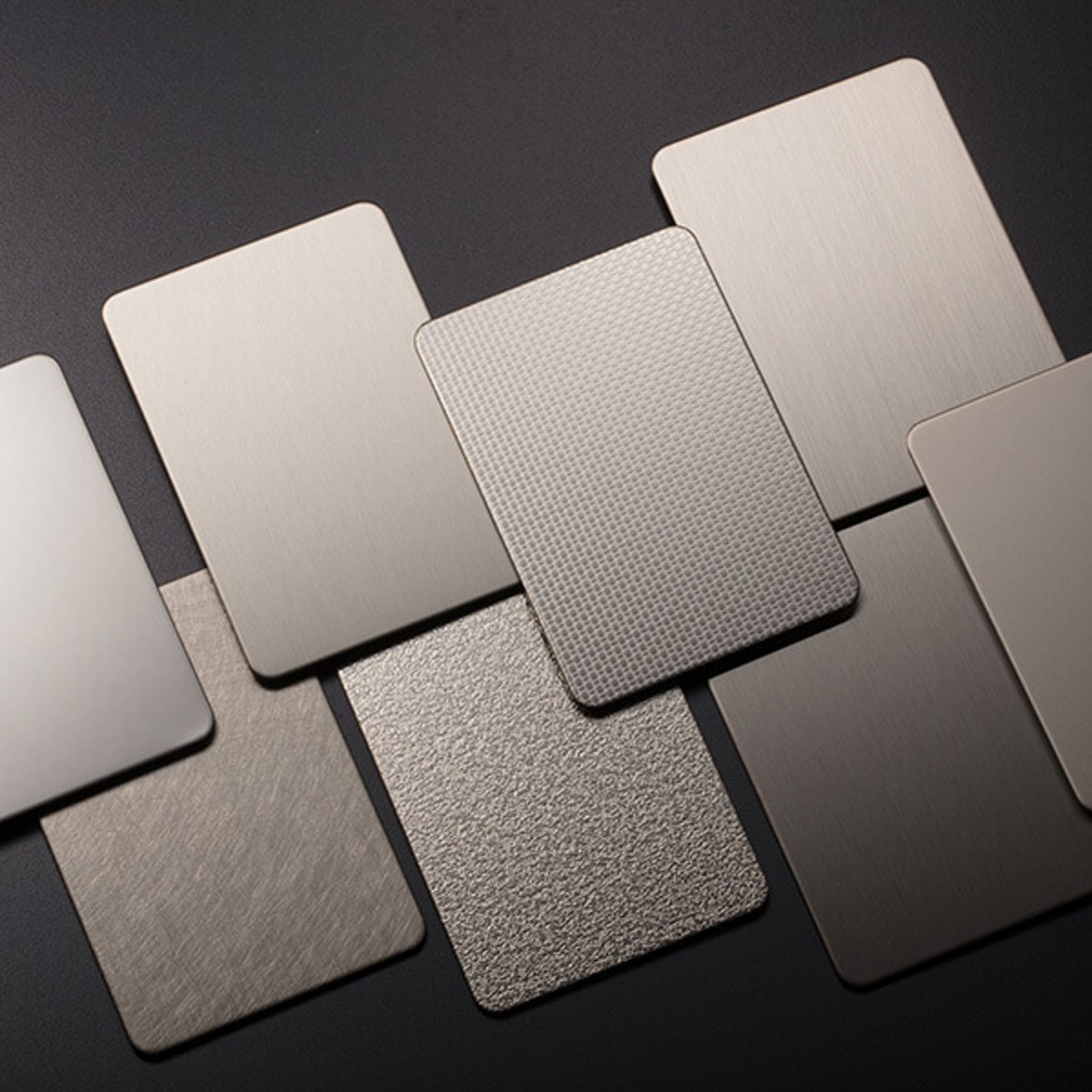
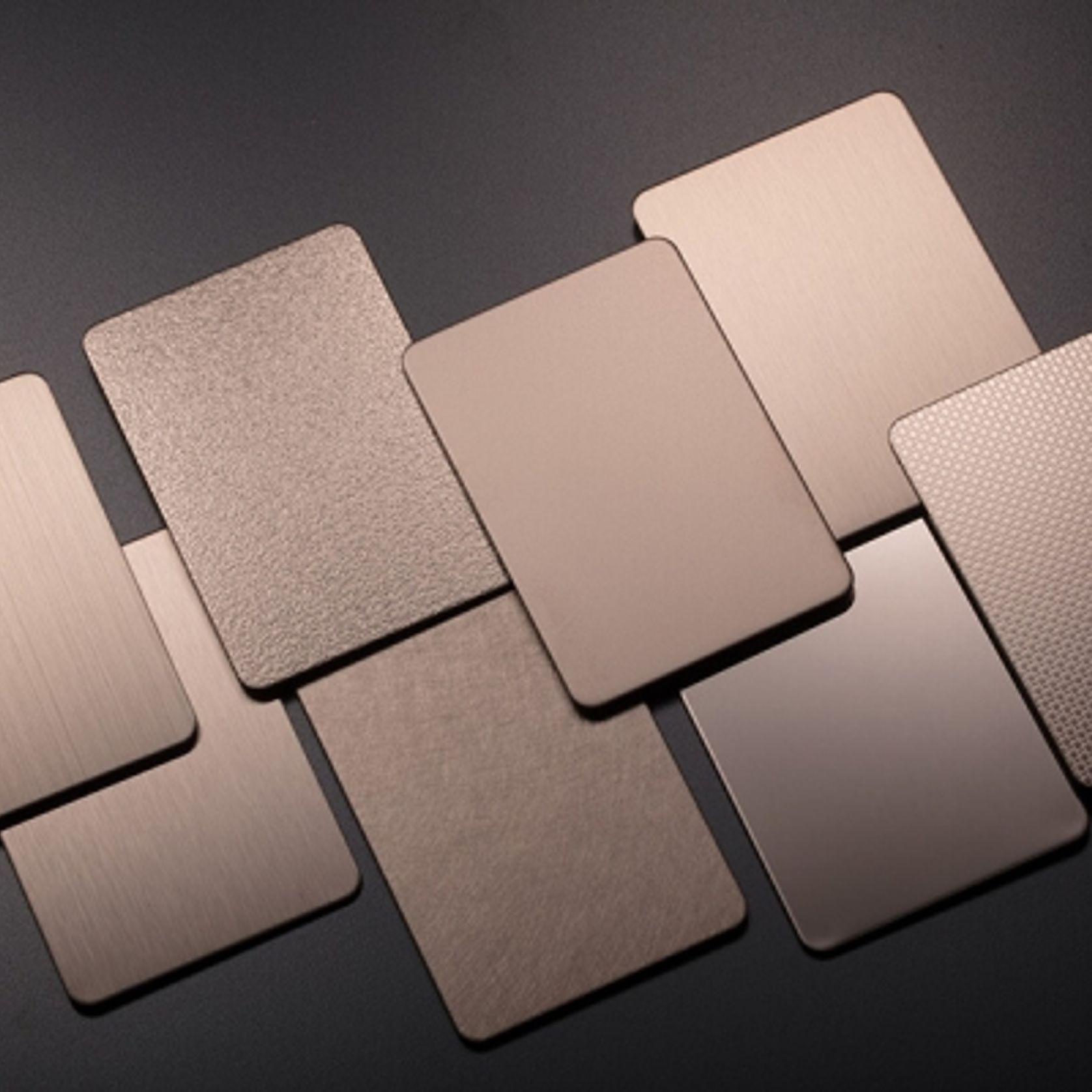
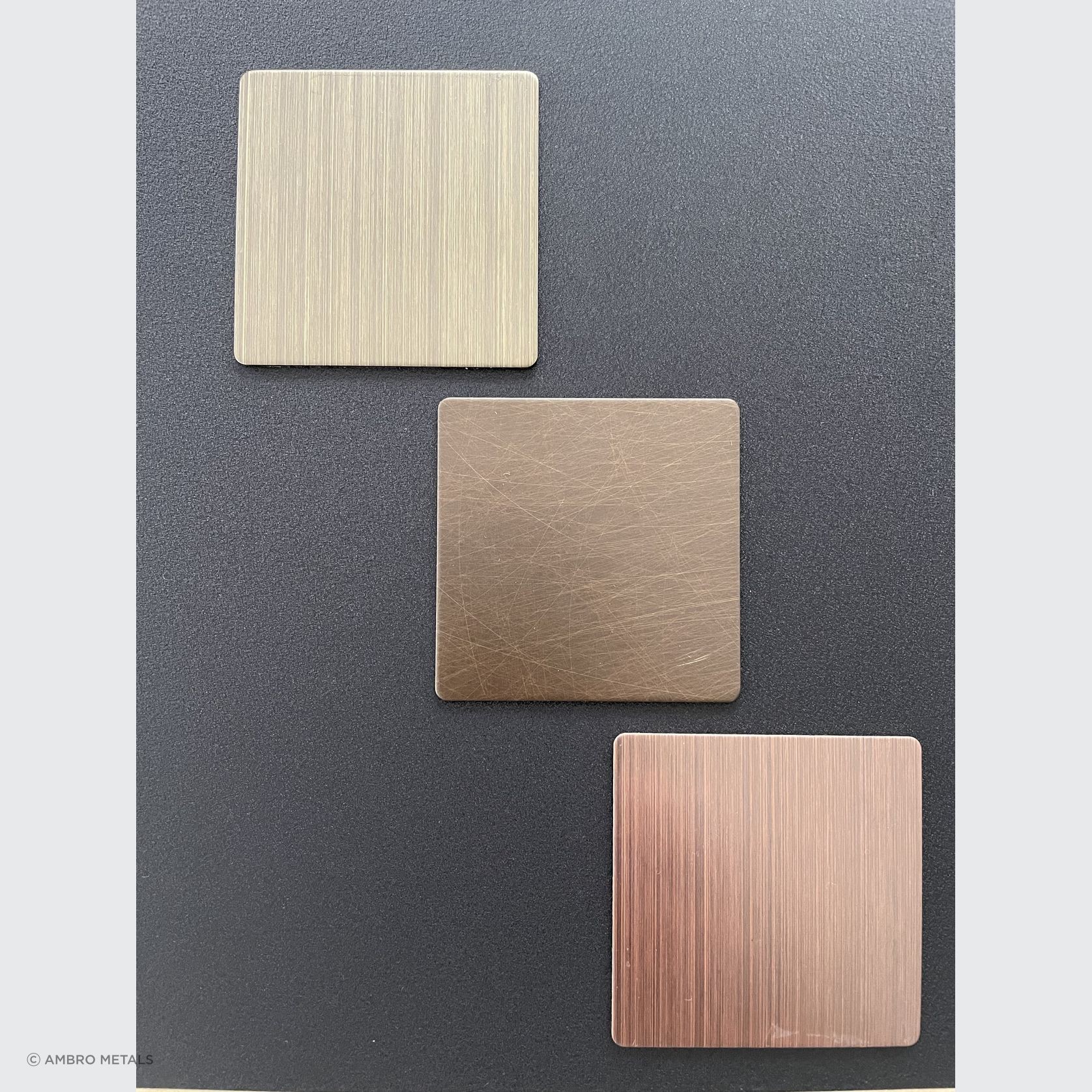
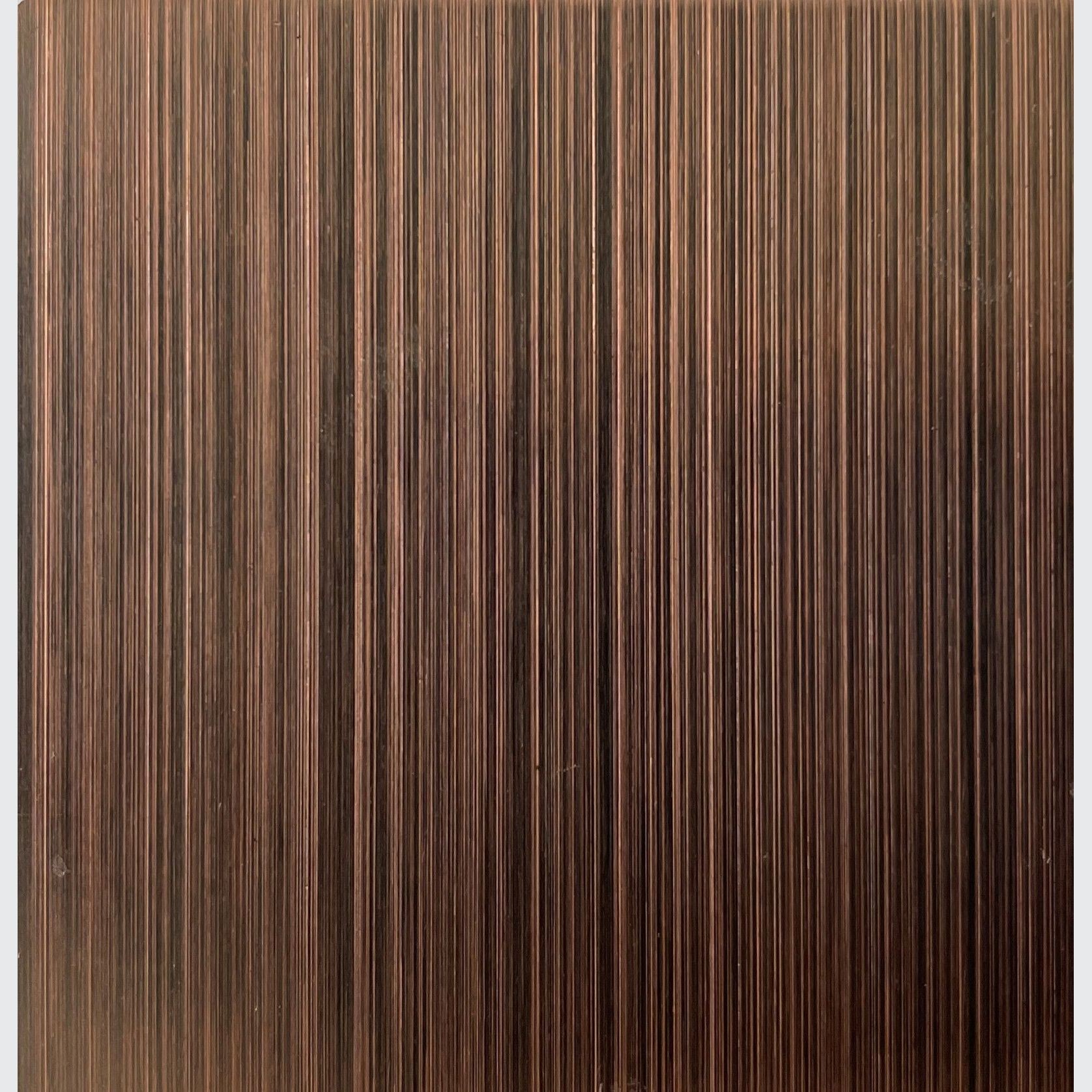
PVD Stainless Steel
Ambro MetalsDetails
- CategoryMetal Roofing, Wall Panels & Cladding , Metal Cladding
- RangeArchitectural Stainless Steel
- Warranty20 years
Scope of use
Performance
Thanks for your inquiry, please provide your email address and we will respond directly.
Visit Website
Downloads
Other products in this range
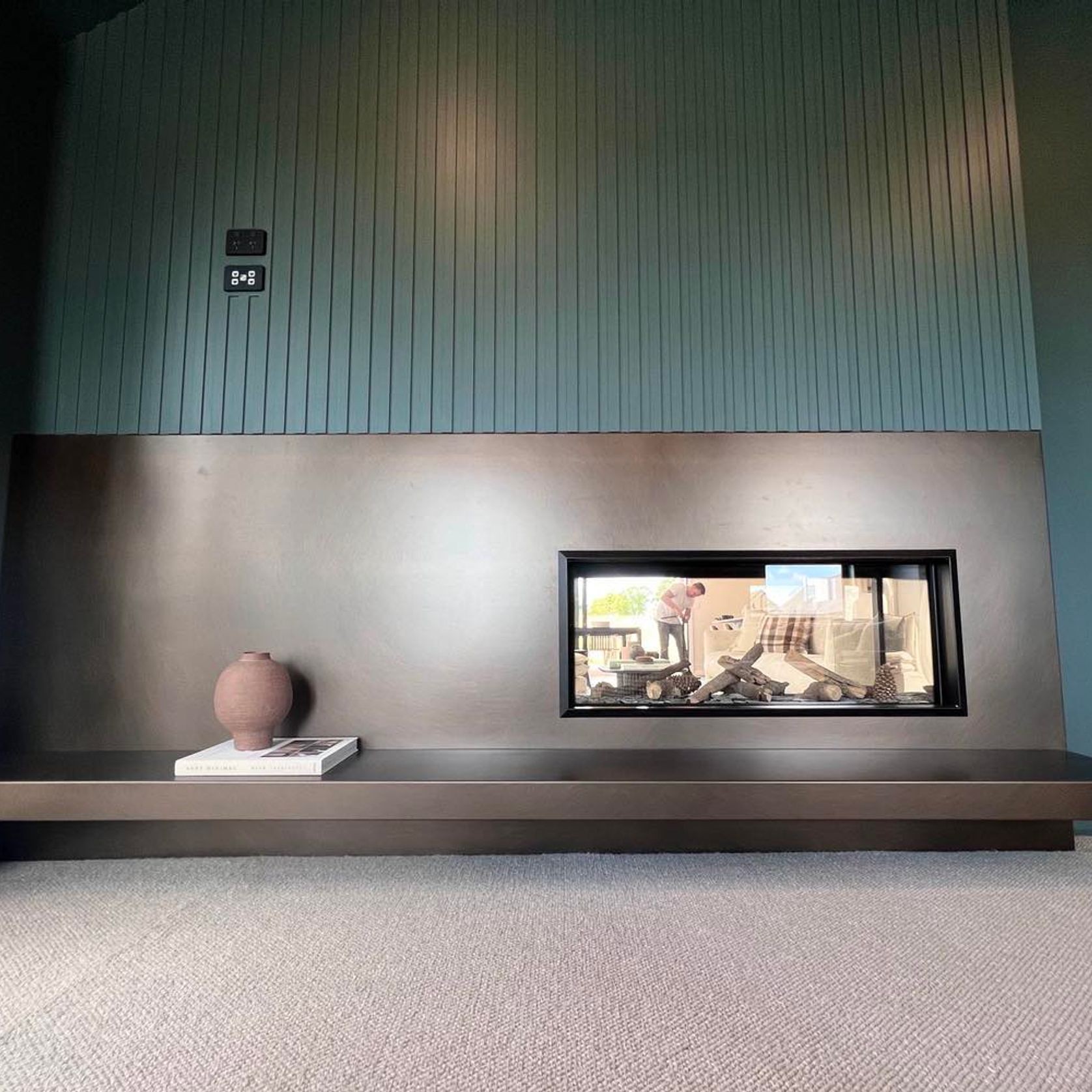
Projects featuring PVD Stainless Steel
About the
Seller
Established in 1981 and based in Avondale, Auckland. Ambro Metals Ltd offers a wealth of experience in the sourcing and the supply of high quality Architectural and Industrial non-ferrous Metals.
We aim to provide long term, innovative, sophisticated Architectural Metal Solutions with strong warranties to meet the demands of local environments. Many years of success in servicing a wide range of industries has given us a solid foundation to help establish a new range of products for the New Zealand market.
Working closely with our network of respected suppliers around the world, we offer our customers a comprehensive range of stock and supply solutions to meet their requirements.
If you are after advice or have any queries, get in touch.
- ArchiPro Member since2015
- LocationView address
- More information